QUESTION 1
Which of the following choices is correct?
A. The entire statement is true
B. Only the statement on conceptual data model is true
C. Only the statement on logical data model is true
D. Only the statement on physical data model is true
Solution
A. The entire statement is true
Explainer »
˙˙˙
The statement describes the typical process of developing data models, which includes progressing from a conceptual data model to a logical data model and, finally, to a physical data model for implementation with a specific database provider.

In an era of rapid globalization and technological advancements, Kasneb's cutting-edge syllabuses are designed to meet the dynamic demands of today's market. Our competency-based approach will boost your global competitiveness and propel you to the pinnacle of success. Join us on the journey to the top!
QUESTION 2

A. Data analysis
B. Data science
C. Statistical inference
D. Predictive modelling
Solution
B. Data science
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Data science encompasses a wide range of activities related to working with data, making it a comprehensive term.
It includes data analysis, statistical inference, predictive modeling, and other data-related tasks.
Data science is the most appropriate choice because it covers the entire field, making it the best fit for the diagram.
Data Analysis (A) - Why it's not as suitable:
Data analysis is an essential component of data science, but it represents only one aspect of the broader field.
The diagram implies a more comprehensive term is needed to describe all activities, not just data analysis.
Statistical Inference (C) - Why it's not as suitable:
Statistical inference is a valuable part of data science, particularly in drawing conclusions from data.
However, data science involves many other activities beyond statistical inference, such as data cleaning, machine learning, and more.
Predictive Modeling (D) - Why it's not as suitable:
Predictive modeling is a significant element within data science, especially for making predictions based on data.
Nonetheless, data science encompasses a broader spectrum of tasks beyond just predictive modeling, such as data exploration and feature engineering.
QUESTION 3
A. Obtaining data and information from different sources, processing and storing for future reference
B. Fixing or removing incorrect, corrupted, incorrectly formatted data and information
C. Collecting data and information about business requirements from stakeholders and end users
D. Creating a visual representation of either a whole information system or parts of it to communicate connections between data points and structures
Solution
D. Creating a visual representation of either a whole information system or parts of it to communicate connections between data points and structures
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Data modeling in the context of CRISP-DM typically refers to the process of designing and creating models that represent the relationships between data points and structures in order to better understand and analyze the data. This can include various types of models, such as entity-relationship diagrams, data flow diagrams, or more complex machine learning models, depending on the specific data mining project.
QUESTION 4
(i) Data mining relates to turning raw data into useful information.
(ii) Data mining using built-in algorithms should guarantee a result.
Which of the following choices apply?
A. The two statements are true
B. Only the first statement is true
C. Only the second statement is true
D. None of the statements is true
Solution
B. Only the first statement is true
Explainer »
˙˙˙
(i) Data mining does indeed relate to the process of turning raw data into useful information. Data mining involves various techniques and algorithms to discover patterns, relationships, or insights within large datasets.
(ii) The second statement is not true. Data mining using built-in algorithms does not guarantee a specific result. The outcome of data mining depends on the data, the algorithms used, and the specific goals of the analysis. While data mining can provide valuable insights, it doesn't guarantee a particular outcome because the results are dependent on the nature of the data and the algorithms applied.
QUESTION 5
A. Veracity
B. Value
C. Variability
D. Variety
Solution
D. Variety
Explainer »
˙˙˙
The "Vs" of data—Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value—are used to describe different characteristics or aspects of data in the context of big data and data analytics. Among these, the "Variety" refers to the diversity and heterogeneity of data types, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Data with multifactor, unstructured, and dynamic attributes falls under the category of data variety.

Study Business Data Analytics Online
Why Business Data Analytics?
Business Data Analytics is essential for informed decision-making in today's competitive landscape. It leverages advanced statistical analysis and data mining techniques to uncover valuable insights, patterns, and trends within large datasets. By interpreting this data, businesses can optimize strategies, improve operational efficiency, and gain a significant competitive advantage, leading to smarter, data-driven decisions.
QUESTION 6
A. Number of children
B. Height of children
C. Behaviour of children
D. Test scores of children
Solution
A. Number of children
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Discrete data consists of distinct, separate values that are typically counted and often involve whole numbers. The number of children is an example of discrete data because it represents a count of individual items (children) and takes on distinct, separate values (0, 1, 2, 3, ...). This is different from continuous data, which can take on any value within a range (like height or test scores).
QUESTION 7
By carrying out risk management and cash budgeting, she is applying:
A. Predictive analytics for risk management and cash budgeting
B. Predictive analytics for risk management and prescriptive analytics for cash budgeting
C. Predictive analytics for cash budgeting and prescriptive analytics for risk Management
D. Prescriptive analytics for risk management and cash budgeting
Solution
B. Predictive analytics for risk management and prescriptive analytics for cash budgeting
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Ms Dare Mongare is using predictive analytics for risk management, which involves analyzing historical data and trends to make predictions about future risks that the company may face.
She is also using prescriptive analytics for cash budgeting, which goes beyond prediction and suggests specific actions or recommendations. In this case, scenario analysis is a form of prescriptive analytics, as it explores different future scenarios and provides guidance on how to handle them.
QUESTION 8
A. Thinking through the potential impacts of our data use on all interested parties
B. Sustainability of the data over time
C. Transparency and inclusivity of the data
D. Data benefiting both the business and customers
Solution
A. Thinking through the potential impacts of our data use on all interested parties
Explainer »
˙˙˙
The principle of Fairness in the Unified Ethical Frame for Big Data Analytics involves considering the potential impacts of data use on all interested parties and ensuring that the use of data does not result in unfair discrimination, bias, or harm to any specific group or individual. It emphasizes the need to treat all stakeholders fairly and equitably when collecting and analyzing data. Option A aligns with this principle by emphasizing the importance of considering the impacts on all parties involved.
QUESTION 9
A. Azure
B. AWS
C. SQL
D. Alibaba Cl
Solution
C. SQL
Explainer »
˙˙˙
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a programming language used for managing and querying relational databases. It is not a cloud computing platform or service in itself. While SQL databases can be hosted on cloud platforms like Azure (A) and AWS (B), SQL itself is not a cloud computing application or service.
Options A, B, and D (Azure, AWS, and Alibaba Cloud) are all examples of cloud computing platforms or services that provide infrastructure, storage, and various other cloud-based solutions.
QUESTION 10
A. Binary
B. Quartenary
C. Unary
D. None of the above
Solution
A. Binary
Explainer »
˙˙˙
In data science and database modeling, the terms "binary", "quaternary" and "unary" are used to describe relationships between entities:
A "binary" relationship is between two entities.
A "quaternary" relationship involves four entities.
A "unary" relationship involves only one entity.
These terms are used to specify the arity or number of entities involved in a relationship within a data model or database schema. However, binary relationships are much more common and widely used in practice compared to quaternary and unary relationships.
QUESTION 11
A. Scatter Graph
B. Bubble Chart
C. Column Chart
D. Line Chart
Solution
B. Bubble Chart
Explainer »
˙˙˙
A bubble chart is a type of data visualization that can effectively present relationships involving more than two variables. It extends the concept of a scatter plot (option A) by adding a third variable that is represented by the size of the bubbles. In a bubble chart, each data point is represented by a bubble, and the position of the bubble on the X and Y axes represents two variables, while the size of the bubble represents a third variable. This allows for the visualization of relationships among three variables simultaneously.
Options C (Column Chart) and D (Line Chart) are useful for presenting data involving one or two variables, but they are not as effective for showing relationships involving more than two variables.
QUESTION 12
A. Line
B. Bar
C. Scatter
D. Histogram
Solution
A. Line
Explainer »
˙˙˙
A line graph displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments. It is commonly used to represent trends or changes over time by connecting data points along the X and Y axes, showing the progression of values and facilitating the visualization of patterns and fluctuations.
QUESTION 13
A. Notify the supervisory authority within 48 hours of the incident whether or not it poses a risk to the organisation and affected individuals
B. Notify the supervisory authority within 48 hours of the incident, only if it poses a risk to the organisation and affected individuals
C. Notify the supervisory authority within 72 hours of the incident whether or not it poses a risk to the organisation and affected individuals
D. Notify the supervisory authority within 72 hours of the incident, only if it poses a risk to the organisation and individuals
Solution
C. Notify the supervisory authority within 72 hours of the incident whether or not it poses a risk to the organisation and affected individuals
Explainer »
˙˙˙
According to data protection laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, in the case of a data breach, the organization should:
C. Notify the supervisory authority within 72 hours of the incident whether or not it poses a risk to the organization and affected individuals.
This means that organizations are generally required to report data breaches to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach, regardless of whether it poses a risk to the organization or affected individuals. Additionally, in some cases, the affected individuals may also need to be notified depending on the severity and impact of the breach.

Release of August 2023 Examination Results
Please access your portal to view your results. We wish you the best of luck
QUESTION 14
A. Data bagging
B. Data dredging
C. Data merging
D. Data pooling
Solution
B. Data dredging
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Data Dredging (also known as data fishing or p-hacking) is a term used to describe the process of analyzing data in a way that involves testing multiple hypotheses without a priori reasoning or a strong theoretical basis. This practice can lead to the discovery of seemingly significant relationships or patterns purely by chance, rather than because they are genuinely meaningful or representative of the underlying data
Data Bagging: Data bagging, also known as bootstrap aggregating or bagging, is a statistical technique used in machine learning to improve the accuracy and stability of a predictive model. It involves taking multiple random samples (with replacement) from the original dataset and training multiple models on these samples. The final prediction is then often based on the majority vote (for classification problems) or averaging (for regression problems) of the predictions made by these models.
Data Merging: Data merging is a process in data management and analysis where two or more datasets are combined into a single dataset. This is typically done when the datasets share common variables, and the goal is to create a unified dataset that contains all the relevant information from the original sources.
Data Pooling: Data pooling refers to the practice of aggregating data from multiple sources or participants into a single dataset for analysis. It is often used in research or business analytics to increase the sample size and improve the statistical power of the analysis. Data pooling can help uncover trends or insights that might not be apparent in smaller individual datasets.
QUESTION 15
EXCEPT on the:
A. Sources of data
B. Data collection
C. Data analysis
D. Assumptions
Solution
C. Data analysis
Explainer »
˙˙˙
The data analyst should be less skeptical about the data analysis itself. Once the data has been collected and properly prepared, the analysis techniques and models used should be based on established principles and methodologies. While critical evaluation is important, once the analysis techniques have been chosen and applied correctly, the results and findings are based on those techniques and should be accepted within the context of their proper application.
QUESTION 16
A. Process data lawfully
B. Maximise data collection
C. Ensure data quality
D. Limit data processing
Solution
B. Maximise data collection
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Data protection laws generally emphasize minimizing data collection and processing to the extent necessary for the stated purposes. The principle is typically to collect and process only the data that is relevant and necessary for the legitimate purposes and to limit excessive data collection.
The other options are in line with common principles of data protection:
Process data lawfully: Data protection laws require that personal data be collected and processed in a lawful and transparent manner, often with the need for consent or a legitimate legal basis.
Ensure data quality: Data protection laws typically require that personal data is accurate and up to date. Organizations are often responsible for ensuring the quality of data they collect and process.
Limit data processing: Data protection laws often impose limitations on the purposes for which data can be processed. Data should only be processed for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
QUESTION 17
A. Providing access to all data to specified employees
B. Providing access to selected data to all employees
C. Restricting access to all data for specified employees
D. A database management system
Solution
D. A database management system
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Implementing a database management system (DBMS).
A database management system is a software application that manages and organizes data, making it more accessible and efficient to retrieve. It helps optimize data storage, retrieval, and processing, which can improve data access speed. Furthermore, a well-designed DBMS can also help in implementing data access controls and restrictions, which addresses the issue of providing or restricting access to specific employees or data as needed for security and compliance purposes.
QUESTION 18
A. Numpy
B. Git
C. Scipy
D. Loft
Solution
B. Git
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Git is an open-source distributed version control system that is widely used for tracking changes in source code during software development. It allows multiple developers to collaborate on a project while keeping track of revisions and changes to the codebase. Numpy and Scipy are libraries for scientific computing in Python, and Loft does not appear to be a known version control system.
QUESTION 19
A. Data management tool
B. Data cleaning tool
C. Data visualisation tool
D. Data presentation tool
Solution
A. Data management tool
Explainer »
˙˙˙
Alteryx is primarily known as a data management and analytics platform that provides a range of data integration, data cleaning, data preparation, and data transformation capabilities. It allows users to manipulate and prepare data for analysis and reporting, making it a data management tool. While it may be used in conjunction with data visualization and presentation tools, its primary focus is on data management and data preparation.
QUESTION 20
A. =sum (A1:H20)
B. =sum (A1:A20)
C. =sum (A1;H20)
D. =sum (A:A20)
Solution
B. =SUM(A1:A20)
Explainer »
˙˙˙
This formula will calculate the sum of the values in cells A1 through A20, providing a subtotal for the variables listed in a vertical range.
SECTION II – TOTAL 60 MARKS
QUESTION 21
| Sepetuka Limited Statement of profit or loss extract for the year ended 30 September: |
||||
| Year Sales Cost of sales Gross profit Operating expenses Operating profit Depreciation Profit before interest and tax Finance costs Profit before tax Income tax expense Profit after tax |
2019 Sh.“000” 54,000 (32,400) 21,600 (10,800) 10,800 (600) 10,200 (5,000) 5,200 (1,560) 3,640 |
2020 Sh.“000” 64,800 (32,400) 32,400 (10,125) 22,275 (800) 21,475 (7,000) 14,475 (4,343) 10,132 |
2021 Sh.“000” 81,000 (32,400) 48,600 (21,094) 27,506 (750) 26,756 (9,000) 17,756 (5,327) 12,429 |
2022 Sh.“000” 95,580 (38,232) 57,348 (14,934) 42,414 (900) 41,514 (8,000) 33,514 (10,054) 23,460 |
Required:
| (a) | Calculate and interpret the following ratios: | |
| (i) | Annual revenue growth rates for years 2020, 2021 and 2022. Explainer » ˙˙˙
|
|
| (ii) | Three years cumulative average growth rate (CAGR) for year 2022. Explainer » ˙˙˙
CAGR = (EV / BV) ^ (1 / n) - 1 Where:
|
|
| (iii) | Effective tax rate for the period 2019 to 2022. Explainer » ˙˙˙
|
|
| (b) | Now assume the following for Sepetuka Limited: | |
| 1. | The revenue growth rate for the first year forecast is the 2022 CAGR. This is expected to reduce by 2% annually | |
| 2. | Gross profit margin for the first year of the forecast is the 3-year average for the period from year 2020 to year 2022. This is expected to reduce by 2% annually until the last year of the forecast subject to a minimum of 50%. |
|
| 3. | Operating expense ratios are modelled as 3-year averages for the period from 2020 to 2022. These are assumed to remain constant over the forecast period. |
|
| 4. | Depreciation to revenue ratio is assumed to remain constant as the 3-year average for the period 2020 to 2022. | |
| 5. | Finance costs are expected to reduce steadily as the loans are repaid. Use the reduction rate in year 2022 over the forecast period. |
|
| 6. | Income tax expense is calculated as the historical effective tax rate. | |
| Required: Prepare five-year forecast statements of profit or loss for Sepetuka Limited from year 2023 to year 2027. |
||
˙˙˙
Workings:
W1
| Operating expenses Total 3-year averages |
2020 2021 2022 |
10,125 / 64,800 x 100% = 15.63% 21,094 / 81,000 x 100% = 26.04% 14,934 / 95,580 x 100% = 15.62% 57.29 57.29/3 = 19.10% |
W2
| Depreciation to revenue Total 3-year averages |
2020 2021 2022 |
800 / 64,800 x 100% = 1.23% 750 / 81,000 x 100% = 0.93% 900 / 95,580 x 100% = 0.94% 3.1 3.1/3 = 1.03% |
W3
| Finance reduction rate | 2022 | (8,000 - 9,000) / 9,000 = 11.11% |
| Revenue growth Gross Profit Margin Operating Expenses Depreciation to Revenue Finance reduction rate Tax Rate |
2023 21% 56.67% 19.10% 1.03% 11.11% 30% |
2024 19% 54.67% 19.10% 1.03% 11.11% 30% |
2025 17% 52.67% 19.10% 1.03% 11.11% 30% |
2026 15% 50.67% 19.10% 1.03% 11.11% 30% |
2027 15% 50.00% 19.10% 1.03% 11.11% 30% |
| Forecast statements of profit or loss for Sepetuka Limited from year 2023 to year 2027. |
|||||
| Year Sales Cost of sales Gross profit Operating expenses Operating profit Depreciation Profit before interest and tax Finance costs Profit before tax Income tax expense Profit after tax |
2023 Sh.“000” 115,651.80 (50,115.78) 65,536.02 (22,086.25) 43,449.77 (1,195.88) 42,253.89 (7,111.11) 35,142.78 (10,542.83) 24,599.94 |
2024 Sh.“000” 137,625.64 (62,390.29) 75,235.35 (26,282.64) 48,952.71 (1,423.10) 47,529.61 (6,320.99) 41,208.63 (12,362.59) 28,846.04 |
2025 Sh.“000” 161,022.00 (76,217.08) 84,804.92 (30,750.68) 54,054.24 (1,665.03) 52,389.21 (5,618.66) 46,770.55 (14,031.17) 32,739.39 |
2026 Sh.“000” 185,175.30 (91,353.15) 93,822.15 (35,363.29) 58,458.87 (1,914.78) 56,544.08 (4,994.36) 51,549.72 (15,464.92) 36,084.81 |
2027 Sh.“000” 212,951.60 (106,475.80) 106,475.80 (40,667.78) 65,808.02 (2,202.00) 63,606.02 (4,439.43) 59,166.59 (17,749.98) 41,416.61 |
QUESTION 22
Additional information:
| 1. | Trex is estimated to have a shelf life of five years commencing year 2023 |
| 2. | Trex will require the purchase of a machine at a cost of Sh 100 million at the end of year 2022, after which the machine will be sold for Sh.20 million at the end of the fifth year. |
| 3. | The selling price and cost structures of Trex (for the first year 2023) with expected inflation factors are as follows: |
Selling price Material costs Direct labour costs Incremental fixed cost (excludes depreciation) |
Sh. (Per unit) 5,000 2,000 1,000 500 |
Inflation rate (%) - from year 2024 onwards 2% 4% 5% 10% |
| 4. | The company is eligible for capital allowances (depreciation for tax purposes) at the rate of 25% on reducing balance. | ||
| 5. | At the end of the project when the machine is sold, any gain or loss on disposal will be considered for tax. | ||
| 6. | The tax rate on income and capital allowances is at the rate of 30% per annum. Assume that the tax for a given period is paid in the same year. | ||
| 7. | The project will require an initial investment in working capital of Sh.20 million which will be increasing by Sh.5 million at the end of each year to cater for general inflation. The whole amount together with the periodic increase will, however, revert at the end of the project. | ||
| 8. | Experience has shown that demand for new products is not exactly known in year one but tends to be stable
thereafter. Jane has come up with the following estimates of demand for year 2023
Jane expects an initial increase in demand in year 2024 of 25% then a decline of 50% in year 2025. This level will remain the same till the end of the project |
||
| 9. | Vuma Limited has a real weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of 8% and general inflation is expected to be at 4%. Due to the risk of the project, Jane feels that the relevant nominal WACC should be increased by 3% | ||
| Required: Compute the following |
|||
| (a). | The weighted average cost of capital to be used to evaluate the project. (2 marks) | ||
| (b). | The relevant cash flows over the project period. (15 marks) | ||
| (c). | The net present value (NPV) of the project. Advise on the viability of the project. | ||
˙˙˙
Coming Soon!
QUESTION 23
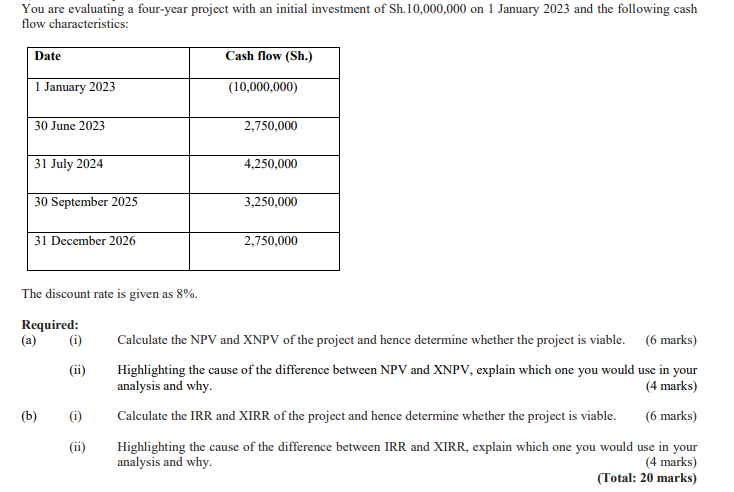
˙˙˙
Coming Soon!
QUESTION 24
.png)
.png)
.png)
˙˙˙
| BAMUDA LIMITED STATEMENT OF CASHFLOW FOR THE YEAR END 30 JUNE 2022 |
|
| OPERATING ACTIVITIES PROFIT BEFORE TAX ADJUSTMENT: DEPRECIATION IMPAIRMENT LOSS 50 - 40 LOSS ON DISPOSAL FINANCE COST GAIN ON FINANCIAL ASSET INVESTMENT INCOME CHANGES IN WORKING CAPITAL TRADE RECEIVABLES 87 - 95 INVENTORY 176 - 123 TRADE PAYABLES 156 - 100 INCREASE IN ASSET AT FAIR VALUE (30 + 5) - 65 CASHFLOW FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES LESS TAX PAID 19 - 34 - 47 NET CASHFLOW FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES INVESTING ACTIVITIES DISPOSAL OF PPE ACQUISITION OF PPE 264 - 43 - 28 - (67 - 36) - 327 ACQUISITION OF FINANCIAL ASSET THROUGH OCI 10 + 2 - 22 INVESTMENT COST CASHFLOW FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES FINANCING ACTIVITIES ISSUE OF SHARES 230 - 150 - 50 ISSUE OF SHARES AT PREMIUM 30 - 0 FINANCE COST PAID 7 - 3 - 17 DIVIDEND PAID 121 - 91 - 67 NET CASHFLOW FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES CASH AND CASHEQUIVALENT A + B + C CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENT B/D CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENT C/D |
SH."MILLION" 114 43 10 6 17 (5) (6) (8) 53 56 (30) 250 (62) 188 (A) 22 (165) (10) 6 (147) (B) 30 30 (13) (37) 10 (C) 51 (22) 29 |
QUESTION 25
.png)
.png)
˙˙˙
Coming Soon!
Comments on:
CPA past papers with answers
BUSINESS DATA ANALYTICS- DECEMBER 2022.
Table of contents
Business Data Analytics - Past Papers
 |
Business Data Analytics Pilot 2022 |
 |
Business Data Analytics December 2022 |
 |
Business Data Analytics April 2023 |
Syllabus
-
1.0
Introduction to Excel
- Microsoft excel key features
- Spreadsheet Interface
- Excel Formulas and Functions
- Data Analysis Tools
- keyboard shortcuts in Excel
- Conducting data analysis using data tables, pivot tables and other common functions
- Improving Financial Models with Advanced Formulas and Functions
-
2.0
Introduction to data analytics
-
3.0
Core application of data analytics
- Financial Accounting And Reporting
- Statement of Profit or Loss
- Statement of Financial Position
- Statement of Cash Flows
- Common Size Financial Statement
- Cross-Sectional Analysis
- Trend Analysis
- Analyse financial statements using ratios
- Graphs and Chats
- Prepare forecast financial statements under specified assumptions
- Carry out sensitivity analysis and scenario analysis on the forecast financial statements
- Data visualization and dash boards for reporting
- Financial Management
- Time value of money analysis for different types of cash flows
- Loan amortization schedules
- Project evaluation techniques using net present value - (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR)
- Carry out sensitivity analysis and scenario analysis in project evaluation
- Data visualisation and dashboards in financial management projects
-
4.0
Application of data analytics in specialised areas
- Management accounting
- Estimate cost of products (goods and services) using high-low and regression analysis method
- Estimate price, revenue and profit margins
- Carry out break-even analysis
- Budget preparation and analysis (including variances)
- Carry out sensitivity analysis and scenario analysis and prepare flexible budgets
- Auditing
- Analysis of trends in key financial statements components
- Carry out 3-way order matching
- Fraud detection
- Test controls (specifically segregation of duties) by identifying combinations of users involved in processing transactions
- Carry out audit sampling from large data set
- Model review and validation issues
- Taxation and public financial management
- Compute tax payable for individuals and companies
- Prepare wear and tear deduction schedules
- Analyse public sector financial statements using analytical tools
- Budget preparation and analysis (including variances)
- Analysis of both public debt and revenue in both county and national government
- Data visualisation and reporting in the public sector
-
5.0
Emerging issues in data analytics